Technology & AI

Radzivon Alkhovik
Jul 17, 2025

The manager of a mid-sized manufacturing company faced typical growing business problems: employees spent hours on routine tasks, customers complained about slow service, and document management errors led to financial losses. After phased implementation of key process automation, the company reduced order processing time by four times, decreased errors by 80%, and increased profit by 35% with the same number of employees.
Business automation involves implementing technological solutions to perform repetitive tasks without human participation or with minimal oversight. Properly implemented automation not only saves time and resources but also improves work quality, reduces errors, and creates opportunities for business scaling.
What is Business Process Automation

Business process automation includes using technologies to perform routine tasks, manage information flows, and coordinate work between different company departments. The goal of automation is to increase efficiency and work quality while reducing time and resource costs.
Definition and Core Principles
Business process automation is the application of technological solutions to replace manual operations with automatic ones, allowing faster task completion, fewer errors, and freeing employees for more important work.
Modern automation is based on principles of systematicity, scalability, and adaptability. Effective solutions integrate with existing systems, can grow with the business, and adapt to changing requirements.
The key principle of successful automation is to first optimize the process, then automate it. Automating an inefficient process only accelerates getting unsatisfactory results.
Types of Business Automation
Modern business uses various types of automation depending on activity specifics and company goals.
Main types of automation:
Operational automation — automating routine operations and procedures
Document management automation — electronic document exchange and processing
Sales and marketing automation — CRM, email campaigns, lead generation
Financial automation — accounting, reporting, management analytics
Production automation — manufacturing process management
Choosing automation type depends on industry, company size, and strategic goals. Maximum effect is achieved with a comprehensive approach and phased implementation of various solutions.
Differences from Digitalization and Optimization
Automation is often confused with digitalization and process optimization, though these are different concepts. Digitalization involves converting information and processes to digital format but doesn't necessarily automate them.
Process optimization aims to improve existing procedures and may not include technological solutions. Automation uses technologies to replace human labor in task execution.
Best results are achieved by combining all three approaches: first optimize the process, then convert to digital format and automate with appropriate technologies.
Why Business Process Automation is Needed
Automation solves multiple modern business tasks and creates the foundation for sustainable growth and development in conditions of growing competition.
Time and Resource Savings
The main value of automation lies in freeing employees from routine tasks and redirecting their efforts to strategically important work. Automatic systems can work 24/7 without weekends and vacations.
Operational cost reduction happens through optimizing resource use, reducing task completion time, and decreasing need for additional personnel for growing work volumes.
Process acceleration allows faster response to customer requests, shorter order fulfillment time, and increased market competitiveness. Many companies achieve process acceleration by several times.
Reducing Human Error
Automated systems perform tasks with high accuracy and consistency, eliminating human factor influence on routine operations. This is critically important for processes where errors can lead to financial losses.
Process standardization through automation ensures uniform task execution regardless of which employee handles them. This improves result quality and simplifies control.
Documentation and audit become automatic, which is important for compliance with legal requirements and internal quality standards. All actions are recorded in the system with time stamps and responsible persons.
Scaling and Efficiency Growth
Automated systems easily scale with business growth without proportional increase in personnel costs. This creates a foundation for sustainable company development.
Released resources can be directed toward developing new business directions, improving product or service quality, customer work, and other strategically important tasks.
Competitiveness increase happens through product cost reduction, customer service process acceleration, and ability to offer more attractive cooperation terms.
Where to Start Business Automation
Successful automation begins with thorough analysis of existing processes and determining priorities for implementing technological solutions.
Process | Implementation Complexity | Potential ROI | Implementation Timeline |
Email campaigns | Low | 200-400% | 1-2 weeks |
Customer management (CRM) | Medium | 150-300% | 1-3 months |
Document management | Medium | 100-250% | 2-4 months |
Financial accounting | High | 120-200% | 3-6 months |
Production processes | Very high | 150-400% | 6-12 months |
HR management | Medium | 80-150% | 2-4 months |
Current Process Audit and Analysis
Comprehensive business process audit identifies bottlenecks, inefficient operations, and automation opportunities. It's important to document existing processes before changing them.
Time cost analysis shows which tasks take most employee time and can be automated with greatest effect. Often significant working time is spent on routine operations.
Identifying pain points helps understand where automation can provide maximum return. These might be processes with high error risk, lengthy approvals, or tasks requiring large data volume processing.
Process Prioritization for Automation
Choosing processes for priority automation should be based on balance between potential effect and implementation complexity.
Criteria for selecting automation processes:
Execution frequency — the more often a process is executed, the greater the automation savings
Execution time — lengthy processes give greater acceleration effect
Number of participants — processes with multiple executors are harder to automate
Standardization — clearly regulated processes are easier to automate
Business criticality — important processes require special attention during automation
It's recommended to start with simple processes that can be quickly automated to get initial results. Successful cases motivate the team and create foundation for more complex projects.
Goal Setting and KPIs
Clear automation goal definition helps choose right solutions and measure implementation results. Goals should be specific, measurable, and time-bound.
Key performance indicators should reflect main automation benefits: time savings, error reduction, productivity growth, and customer service quality improvement.
Baseline metrics must be recorded before automation starts to objectively evaluate results. Regular indicator measurement helps adjust the implementation process.
Automation Implementation Stages
Phased automation implementation approach reduces risks and ensures smoother transition to new working methods.
1. Planning and Team Preparation
Detailed automation project planning includes determining budget, timeframes, responsible persons, and success criteria. It's important to consider all implementation aspects, including staff training and existing system integration.
Team preparation begins with explaining automation goals and benefits. Employees should understand that technologies are meant to help them work more efficiently, not replace them.
Appointing project managers ensures action coordination and plan execution control. It's advisable to choose people who understand automated processes well and have team authority.
2. Tool and Technology Selection
Choosing appropriate automation tools depends on business specifics, project budget, and technical requirements. It's important to evaluate not only functionality but also ease of use, reliability, and integration capabilities.
Companies should consider data protection legislation requirements and possible restrictions on using foreign software. Many tasks can be solved with domestic solutions.
Solution scalability is critically important for growing companies. It's better to choose a system that can develop with the business than periodically change tools during expansion.
3. Pilot Implementation and Testing
The pilot project allows testing chosen solutions on a limited work area and identifying possible problems before full-scale implementation. This reduces risks and allows approach correction.
Testing should include checking all system operation aspects: functionality, performance, integration with other systems, and ease of use. It's important to get user feedback.
Documenting pilot results helps make informed decisions about project continuation and next stage planning. A successful pilot becomes the foundation for solution scaling.
4. Scaling and Staff Training
Gradual automation expansion to other processes and departments ensures controlled transition and timely approach correction opportunity.
Staff training should be comprehensive and include not only technical preparation but also explanation of workflow changes. Effective training significantly accelerates adaptation to new tools.
Technical support during implementation helps quickly resolve arising questions and problems. It's important to ensure help availability, especially in the first weeks of new system use.
Business Automation Tools
The modern market offers a wide spectrum of tools for automating various business aspects — from simple solutions for small business to comprehensive corporate platforms.
CRM and Customer Management Systems
CRM systems automate customer relationship management from first contact to after-sales service. Modern CRMs integrate with email, telephony, websites, and social networks.
Sales automation includes funnel management, result forecasting, automatic reminders and tasks for managers. This increases team efficiency and reduces probability of losing customers.
CRM analytics and reporting provide data on team performance, customer sources, and promotion channel effectiveness. This helps make informed business development decisions.
ERP and Resource Planning
ERP systems unite management of all enterprise resources: finances, personnel, production, procurement, and sales. Comprehensive automation ensures all process coordination.
Supply chain management automates procurement planning, inventory control, supplier work, and logistics optimization. This reduces costs and increases production reliability.
Financial planning and accounting become more accurate through data integration from all departments. Automatic report generation saves time and reduces error probability.
Marketing and Sales Automation
Marketing automation includes lead management, email campaigns, content personalization, and analytics of different customer attraction channel effectiveness.
Automatic sales funnels guide potential customers through interaction sequences adapted to their behavior and interests. This increases conversion and reduces sales team load.
Retargeting and personalization help retain potential customer attention and increase purchase probability. Automatic systems track user behavior and offer relevant content.
Workflow and Task Management
Workflow management systems automate approvals, confirmations, and task transfers between employees. This accelerates project completion and increases process transparency.
Automatic task distribution is based on employee workload, competencies, and project priorities. This optimizes team resource use.
Deadline control and automatic reminders help avoid deadline disruptions and ensure timely client obligation fulfillment.
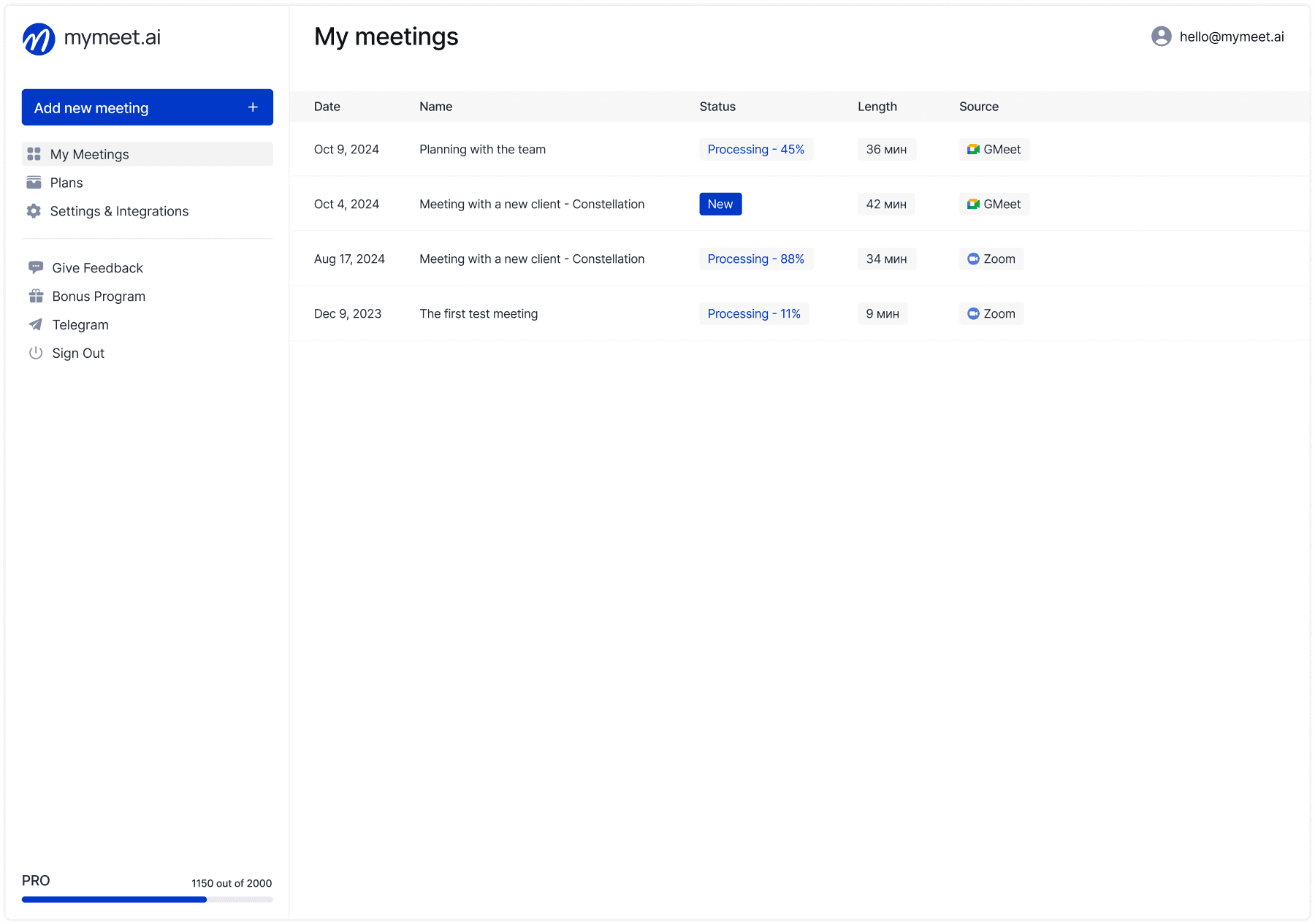
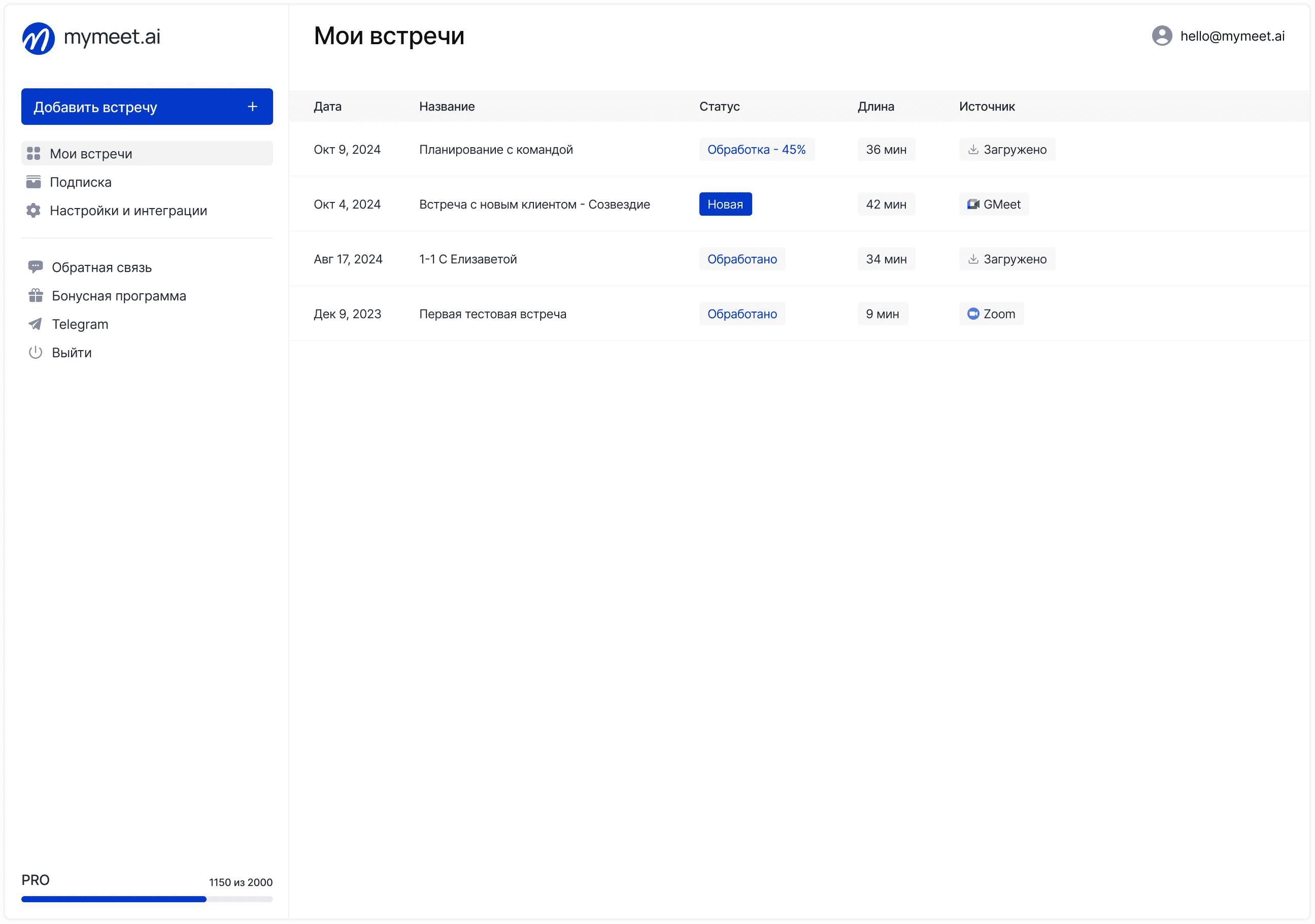
mymeet.ai for Business Meeting Automation

The mymeet.ai platform automates one of the most time-consuming business processes — analyzing and documenting business meetings, freeing employees from routine work of creating protocols and reports.

Key automation capabilities with mymeet.ai:
✅ Automatic meeting transcription — converting speech to text with high accuracy in multiple languages
✅ AI content analysis — automatic highlighting of key topics, decisions, and tasks from conversations

✅ Meeting protocol creation — generating structured reports without human participation
✅ Task and deadline extraction — automatic identification of assignments with responsible persons and deadlines
✅ CRM integration — automatic updating of customer cards with meeting data
✅ Efficiency analytics — analyzing meeting productivity and identifying successful negotiation patterns

✅ Multi-language support — processing meetings in 73 languages for international companies
✅ Enterprise-grade security compliance — secure processing of personal data with enterprise-level security standards
TechFlow Solutions Case: Project Meeting Analysis Automation
TechFlow Solutions, engaged in software development, implemented mymeet.ai to automate project meeting documentation. Before implementation, project managers spent 2-3 hours daily creating protocols and distributing tasks.
After mymeet.ai integration, meeting documentation became completely automatic. AI analyzes discussions, highlights key decisions, and automatically creates task lists with responsible persons and deadlines.
Automation result: saving 15 hours weekly per project manager, improved documentation quality, and reduced forgotten tasks. The team gained the ability to focus on development instead of administrative work.
Train employees to work with the AI assistant. Submit an application via the form for a corporate webinar.

Implementation Automation Mistakes
Understanding typical mistakes helps avoid problems during automation implementation and ensure successful project realization.
Automating Inefficient Processes
One of the most common mistakes is automating processes without preliminary optimization. If a process is initially inefficient, automation only accelerates getting unsatisfactory results.
Before implementing technologies, it's necessary to analyze and optimize existing processes. Often some operations can be simplified or eliminated completely.
The principle "first optimize, then automate" should be the foundation of any project. This allows getting maximum effect from technology implementation.
Ignoring Human Factor
Staff resistance to changes can seriously hinder automation implementation. Employees may fear job loss or complication of their duties.
It's important to explain team goals and automation benefits from the start, emphasizing that technologies are meant to help people work more efficiently, not replace them.
Involving employees in the planning and solution selection process increases their interest in project success. People better accept changes they participated in.
Lack of Result Measurement
Many companies don't establish clear success metrics before automation begins and don't track results after implementation. This makes it difficult to evaluate investment effectiveness.
It's important to determine baseline indicators before project start and regularly measure changes. Metrics should reflect main automation goals: time savings, error reduction, productivity growth.
Result analysis helps identify problems and opportunities for further improvement. Automation effectiveness data is also useful for planning next projects.
Conclusion
Business process automation becomes a necessary condition for competitiveness in the modern economy. Companies that systematically approach technology implementation gain significant advantages in efficiency and work quality.
Successful automation requires careful planning, correct process and tool selection, and competent change management. Phased approach and attention to human factors ensure smooth transition to new working methods.
Start automating your business today: use mymeet.ai to automate business meeting analysis and document management. 180 minutes of free testing will show how artificial intelligence can free your employees from routine tasks and increase team work efficiency.
FAQ about Business Automation
Where to start automation for small businesses?
Start with process audit and identifying the most time-consuming routine tasks. First automate simple processes: email campaigns, customer accounting in CRM, automatic document creation. This gives quick results and experience for more complex projects.
How much does business process automation cost?
Cost depends on project scale and complexity. Simple solutions for small business may cost $3,000-15,000 annually, comprehensive mid-size enterprise automation — from $15,000 to several hundred thousand dollars.
How to measure automation effectiveness?
Main metrics include employee time savings, error count reduction, process execution acceleration, and project ROI. It's important to record baseline indicators before implementation and regularly track changes.
Which processes to automate first?
Priority should go to frequently repeated, standardized processes with high time costs. Good candidates: document management, customer accounting, email communications, report generation.
Do you need to change staff during automation?
Usually retraining existing employees is sufficient. Automation frees people from routine for more important tasks. Layoffs are rarely required, usually only with fundamental business model changes.
How to choose an automation system for your business?
Evaluate functionality, ease of use, integration capabilities, scalability, and total cost of ownership. Always conduct pilot testing before making final decisions.
How long does automation implementation take?
Simple solutions implemented in 1-4 weeks, medium projects — 2-6 months, comprehensive large enterprise automation may take 6-18 months. Phased approach accelerates getting first results.
How to prepare a team for automation?
Explain change goals and benefits, involve employees in planning, ensure quality training on new tools. Appoint project managers from authoritative team members.
What risks exist in business automation?
Main risks: choosing unsuitable solutions, staff resistance, budget overrun, integration problems with existing systems. Phased implementation and careful planning reduce these risks.
Can creative processes be automated?
Full automation of creative processes isn't yet possible, but routine tasks in creative work can be automated: information search, draft creation, formatting, content publishing. AI becomes an assistant for creative specialists.
Radzivon Alkhovik
Jul 17, 2025