Technology & AI

Andrey Shcherbina
Mar 13, 2025

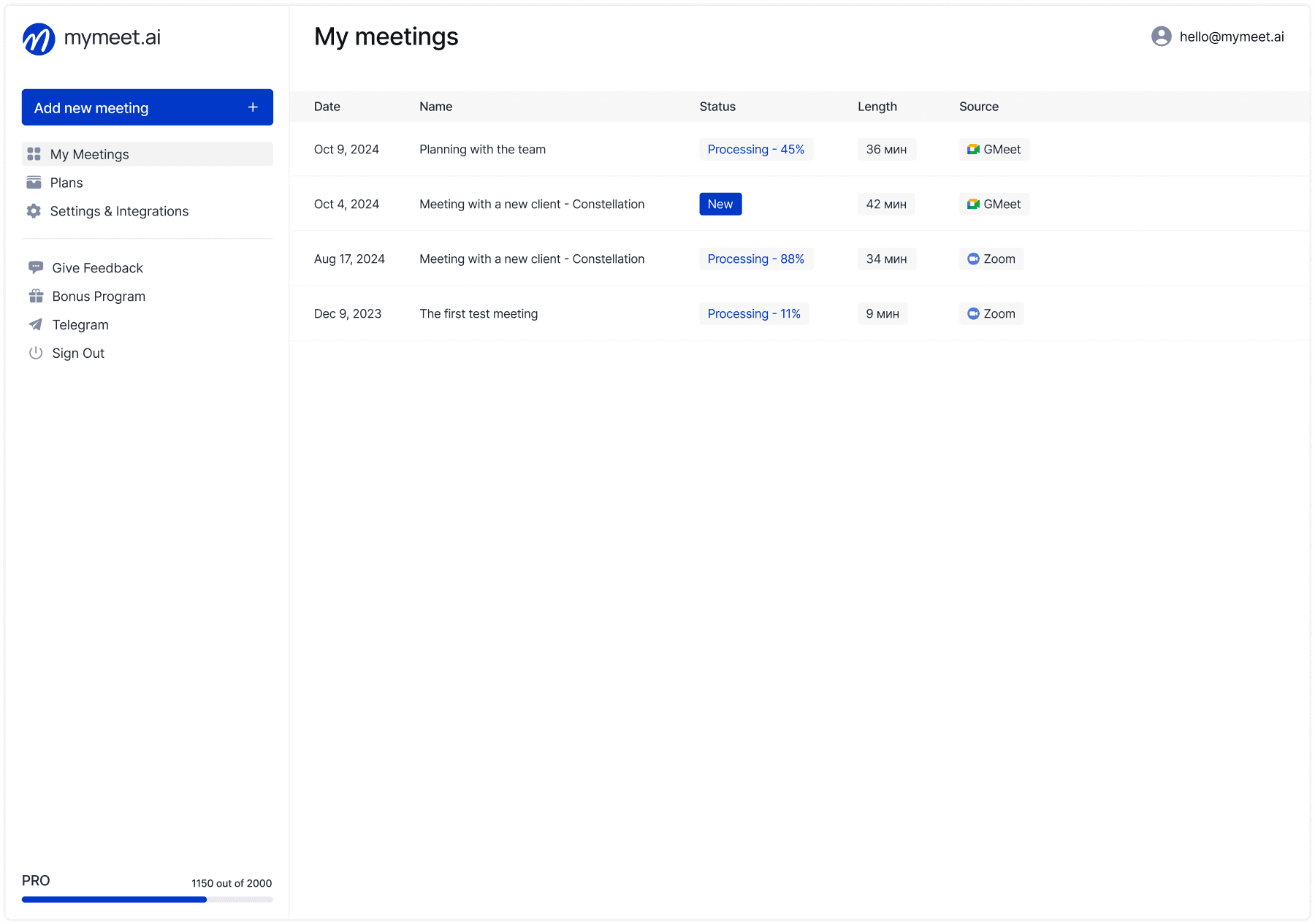
An interview transcript is a textual record of a conversation between an interviewer and a respondent, which converts audio or video into a document. According to Scribie research, accurate transcription increases data analysis efficiency by 67% and saves up to 4 hours of work for each hour of recording.
In an era where video and audio content dominate the digital space, transcripts are becoming an essential tool for researchers, journalists, marketers, and business analysts. They make information accessible for searching, analysis, and citation, which is impossible with audio format.
Standards for Formatting Interview Transcripts
A professional transcript is not just a verbatim record of what was said. There are various formatting standards depending on the purpose of use.
Transcript Type | Characteristics | Best Suited For |
Verbatim | Includes every word, interjections, filler words, repetitions | Linguistic analysis, legal documentation |
Edited | Preserves content accuracy but removes speech errors and repetitions | Journalism, business analysis, marketing research |
Condensed | Contains only key points and important quotes | Executive summaries, briefings, press releases |
Expanded | Includes contextual notes, non-verbal elements | Psychological research, behavior analysis |
Key elements of a professional transcript:
Header with date, time, and participants
Clear identification of speakers (usually "I:" for interviewer, "R:" for respondent or by names)
Timestamps for long recordings (usually every 2-5 minutes)
Notations for pauses, intonations, and non-verbal elements
Markings for confidential information, if required
Example of a Research Interview Transcript
A research transcript is usually the most detailed, including non-verbal elements and contextual notes. Here's an example:
RESEARCH INTERVIEW TRANSCRIPT
Key features:
Detailed information about the interview context
Timestamps for easy navigation
Notation of non-verbal actions in square brackets
Recording of pauses and emotional reactions
Example of a Journalistic Interview Transcript
Journalistic transcripts are usually more edited for ease of reading but maintain the accuracy of statements.
INTERVIEW WITH ANNA SMIRNOVA, CEO OF "INNOVATE" TECHNOLOGY STARTUP
Features of a journalistic transcript:
Clean, edited text without filler words
Minimum non-verbal elements
Clear "question-answer" structure
More concise context information
Use of initials to identify speakers
Example of a Business Interview Transcript
Business meeting and interview transcripts are often structured by topics and include highlighting of key decisions and actions.
DECISIONS MADE AND NEXT STEPS
- Preliminary project budget agreed: 1.2-1.5 million rubles
- By 22.03, the implementation team will audit current processes
- By 30.03, a detailed implementation plan will be presented
- Approximate system launch date: end of May 2025
OPEN QUESTIONS
1. Need for IP telephony integration (IS will clarify before the next meeting)
2. Historical data migration procedure
Features of a business transcript:
Structuring by topics or meeting agenda
Highlighting key decisions and actions
Recording responsible parties and deadlines
Marking open questions for subsequent clarification
Minimum unnecessary details, focus on substantial content
Common Mistakes When Creating Transcripts
Even experienced transcribers make mistakes that can significantly reduce the value of a transcript:
Loss of context — recording only words without important non-verbal elements or emotional reactions
Excessive editing — correcting speech to the point of losing authenticity and original meaning
Inaccurate attribution — incorrect identification of speakers, especially in group discussions
Missing technical terms — distortion of specialized vocabulary due to unfamiliarity with the subject area
Ignoring timestamps — makes it difficult to find needed fragments in long recordings
The most common mistake is trying to make a transcript "pretty" at the expense of accuracy. It's important to remember that the goal of a transcript is to convey the content of the conversation in text format as accurately as possible, preserving speech characteristics that may be significant for analysis.
How to Use Transcripts for Various Purposes
Interview transcripts are a versatile tool that can be applied in multiple scenarios:
Scientific research — coding and thematic analysis of qualitative data
Content marketing — turning interviews into articles, blog posts, white papers
Staff training — creating case studies based on interviews with experts
Knowledge documentation — preserving the expertise of departing employees
Legal purposes — recording testimony and evidence in exact form
Product development — analyzing user interviews to identify requirements
A valuable approach is extracting quotes from transcripts for use in presentations, reports, or marketing materials. Direct speech from research participants or interviewees adds credibility and emotional depth to dry analytics.
Tools and Methods for Creating Transcripts
Interview transcription has evolved from a completely manual process to a highly automated one:
Manual transcription — the most accurate but also the most labor-intensive method (6-10 hours of work per 1 hour of audio)
Programs to facilitate manual transcription (Express Scribe, InqScribe) — offer hotkeys for playback control
Automatic transcription (Google Speech-to-Text, Amazon Transcribe) — fast but requires verification and correction
Hybrid solutions — combining automatic transcription with manual refinement
The main problem with fully automatic solutions is insufficient quality when working with:
Low-quality audio or with background noise
Speech with strong accent or dialect
Specific terminology
Overlapping speech from multiple speakers
How mymeet.ai Transforms the Transcription Process
The mymeet.ai platform represents a new generation of tools for working with interviews, combining automatic transcription with artificial intelligence for content analysis.

Main features of mymeet.ai for working with transcripts:
High-precision automatic transcription — thanks to the use of advanced speech recognition models, the system achieves accuracy up to 95-98% even when working with Russian language

Speaker recognition — automatic division of the transcript by speakers with the ability to specify their names
Intelligent chapter division — AI identifies logical blocks in the conversation, simplifying navigation in long interviews

Content search — ability to find needed information in the transcript by keywords
Highlighting key moments — automatic identification of the most important parts of the conversation
AI chat with the ability to ask questions — after transcription, you can ask the system, for example, "What main problems did the respondent mention?" or "What specific figures were named?"

A particularly valuable function is the ability to clean the transcript of filler words and hesitations while preserving the meaning and style of speech. This saves editing time and makes transcripts immediately ready for use.
Examples of AI-Enhanced Transcripts
Comparing standard and AI-enhanced transcripts shows a significant difference in usability:
Standard transcript:
The enhanced transcript is not only cleaned of filler words but also structured with an indication of the topic, participant positions, and automatic highlighting of key insights.
Ethical Aspects of Using Transcripts
When working with transcripts, it's important to follow ethical principles:
Informed consent — always notify participants about recording and subsequent transcription
Confidentiality — de-identify data if necessary (replacing names, removing sensitive information)
Accuracy — strive for maximum accurate transmission of what was said
Context — preserve contextual information to avoid misinterpretation
Data storage — ensure secure storage of recordings and transcripts
In some cases (for example, when working with children or vulnerable groups), additional ethical permission or special data processing protocols may be required.
Conclusion
Quality interview transcripts are more than just converting audio to text. They are a tool that makes information accessible, structured, and suitable for analysis and further use.
Key principles for creating good transcripts:
Balance between verbatim accuracy and readability
Adaptation of format to specific usage goals
Preservation of important context and non-verbal elements
Use of modern technologies to increase efficiency
The future of transcription belongs to intelligent systems like mymeet.ai, which not only convert speech to text but also help analyze, structure, and extract valuable insights from conversations. Technologies expand the capabilities of researchers, journalists, and business analysts, allowing them to focus on interpreting and using information rather than on the routine aspects of processing it.
Frequently Asked Questions About Interview Transcripts
What transcript format is best for scientific research?
For qualitative research, a verbatim transcript with recording of pauses, intonations, and non-verbal elements is optimal. For content analysis or thematic studies, an edited format that preserves all significant statements but without filler words and repetitions is suitable.
Should filler words and slips of the tongue be included in the transcript?
It depends on the purpose. For linguistic analysis or psychological research — yes. For journalism or business purposes — usually not, unless they change the meaning of the statement or characterize the speaker in an important way.
How long does it usually take to transcribe a one-hour interview?
With manual transcription — from 4 to 8 hours depending on recording quality, speech speed, and transcriber experience. Automatic systems do this in time comparable to the recording duration but require additional time for verification and correction.
Can a transcript be edited to improve readability?
Yes, if it doesn't distort the meaning of what was said. The degree of editing should correspond to the purpose of use. For academic publications, it's customary to indicate that the transcript was edited for clarity.
How to properly mark non-verbal elements in a transcript?
Square brackets with a description of the action or emotion are usually used: [laughs], [pause], [points to chart]. It's important to use a consistent system of notation and, if necessary, attach a legend of the notations used to the transcript.
Andrey Shcherbina
Mar 13, 2025